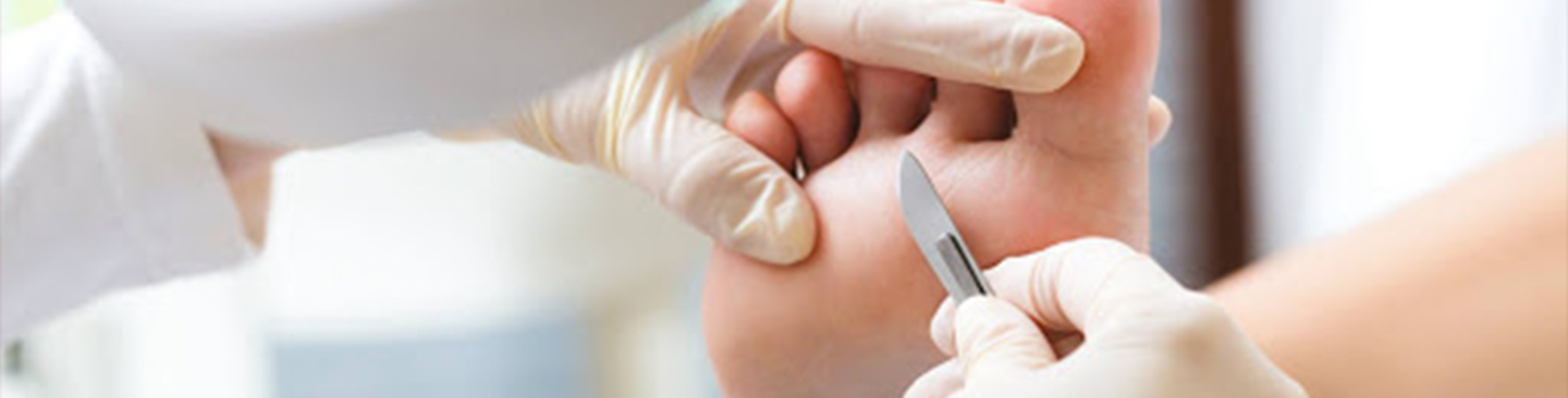
Chiropody (Medical pedicure)
Chiropody medical pedicure is a non-invasive, dry procedure performed by highly skilled foot care specialists who combine podiatry with nail care. Guaranteed to be safe and hygienic, it addresses issues such as: Athlete’s foot. Corns, Ingrown/overgrown toenails.
Foot Problems
Sesamoiditis

Definition:
Sesamoiditis is a common ailment that affects the forefoot, typically in young people who engage in physical activity like running or dancing. Its most common symptom is pain in the ball-of-the-foot, especially on the medial or inner side. The term is a general description for any irritation of the sesamoid bones, which are tiny bones within the tendons that run to the big toe. Like the kneecap, the sesamoids function as a pulley, increasing the leverage of the tendons controlling the toe. Every time you push off against the toe the sesamoids are involved, and eventually they can become irritated, even fractured. Because the bones are actually within the tendons, sesamoiditis is really a kind of tendinitis – the tendons around the bones become inflamed as well.
Treatment:
Treatment for sesamoiditis is almost always noninvasive. Minor cases call for a strict period of rest, along with the use of a modified shoe or a shoe pad to reduce pressure on the affected area. This may be accomplished by placing a metatarsal pad away from the joint so that it redistributes the pressure of weight bearing to other parts of the forefoot. In addition, the big toe may be bound with tape or athletic strapping to immobilize the joint as much as possible and allow for healing to occur. It is recommended to decrease or stop activity for a while. This will give your sesamoids time to heal. You should apply ice to the area for 10 to 15 minutes after exercise, or after any activity that aggravates the area. As with icing, anti-inflammatories will help the swelling go down so healing can begin. While the injury is healing, women should wear flat shoes on a daily basis. If home remedies do not work, see your doctor for a correct diagnosis.
Heel Spurss

Definition:
The heel bone is the largest bone in the foot and absorbs the most amount of shock and pressure. A heel spur develops as an abnormal growth of the heel bone. Calcium deposits form when the plantar fascia pulls away from the heel area, causing a bony protrusion, or heel spur to develop. The plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue located along the bottom surface of the foot that runs from the heel to the forefoot. Heel spurs can cause extreme pain in the rearfoot, especially while standing or walking.
Treatment:
The key for the proper treatment of heel spurs is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation, and allow the condition to heal.
Calluses

Definition:
The formation of calluses is caused by an accumulation of dead skin cells that harden and thicken over an area of the foot. This callus formation is the body’s defense mechanism to protect the foot against excessive pressure and friction. Calluses are normally found on the ball-of-the-foot, the heel, and/or the inside of the big toe.
Treatment:
To relieve the excessive pressure that leads to callus formation, weight should be redistributed equally with the use of an orthotic. An effective orthotic transfers pressure away from the “hot spots” or high-pressured areas to allow the callus to heal. The orthotic should be made with materials that absorb shock and shear (friction) forces.
Plantar fasciitis

Definition:
Plantar Fasciitis is an inflammation caused by excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue which runs along the bottom surface of the foot, attaching at the bottom of the heel bone and extending to the forefoot. When the plantar fascia is excessively stretched, this can cause plantar fasciitis, which can also lead to heel pain, arch pain, and heel spurs.
Treatment:
The key for the proper treatment of plantar fasciitis is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation and allow the condition to heal.
If you have usually high arches, which can also lead to plantar fasciitis, cushion the heel, absorb shock and wear proper footwear that will accommodate and comfort the foot.
Diabetic Foot

Definition:
Diabetes is a serious disease that can develop from lack of insulin production in the body or due to the inability of the body’s insulin to perform its normal everyday functions. Insulin is a substance produced by the pancreas gland that helps process the food we eat and turn it into energy.
Many complications can be associated with diabetes. Diabetes disrupts the vascular system, affecting many areas of the body such as the eyes, kidneys, legs, and feet. People with diabetes should pay special attention to their feet.
Treatment:
Footwear and orthotics play an important role in diabetic footcare. Orthotics designed with Plastazote’ foam, the #1 material for protecting the insensitive diabetic foot, are usually recommended. Plastazote is a material designed to accommodate pressure ‘hot spots’ by conforming to heat and pressure. By customizing to the foot, Plastazote provides the comfort and protection needed in diabetic footcare. Footwear constructed with Plastazote is also recommended frequently for the diabetic patient.
Arch pain/arch strain

Definition:
The term arch pain (often referred to as arch strain) refers to an inflammation and/or burning sensation at the arch of the foot. A structural imbalance or an injury to the foot can often be the direct cause.
Treatment:
This is a common foot condition that can be easily treated. If you suffer from arch pain avoid high-heeled shoes whenever possible. Try to choose footwear with a reasonable heel, soft leather uppers, shock absorbing soles and removable foot insoles. When the arch pain is pronation related (flat feet), an orthotic designed with a medial heel post and proper arch support is recommended for treating the pain. This type of orthotics will control over-pronation, support the arch and provide the necessary relief.
Arthritis is a disease characterized by the inflammation of the cartilage and lining of the body’s joints. Inflammation causes redness, warmth, pain and swelling. There are many different types of arthritis. The most common type is called osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis causes excessive strain and the wearing away of cartilage in the joints of the foot. Movement becomes very difficult and painful. The pain and swelling worsens while standing or walking, and stiffness usually occurs after periods of rest.
Warts

Definition:
Warts on your feet or anywhere on your body are caused by a specific strain of the human papillomavirus or HPV. This virus is easily passed from person to person by direct close contact. It can also be contracted by walking barefoot in public locker rooms and showers. There is no cure for this virus. Warts on feet are a symptom of HPV and they should be treated to prevent pain.
Treatment:
Your doctor should be able to confirm that what you have is really warts on your feet. After the diagnosis he may choose to burn the warts off or he may use a chemical to freeze the warts away. Both treatment methods could end up costing you a significant sum of money, especially if you don’t have health insurance. But this is not your only option for wart removal.
Corns

Definition:
Corns like calluses develop from an accumulation of dead skin cells on the foot, forming thick, hardened areas. They contain a cone-shaped core with a point that can press on a nerve below, causing pain. Corns are a very common ailment that usually forms on the tops, sides and tips of the toes. Corns can become inflamed due to constant friction and pressure from footwear. Corns that form between the toes are sometimes referred to as soft corns.
Treatment:
There are very simple ways to prevent and treat the corns. You should wear properly fitted footwear with extra room in the toe box (toe area). Avoid shoes that are too tight or too loose. Use an orthotic or shoe insert made with materials that will absorb shock and shear forces. Also avoid tight socks and stockings to provide a healthier environment for the foot.
Achilles tendonitis

Definition:
Achilles tendonitis causes inflammation and degeneration of the achilles tendon. The achilles tendon is the large tendon located in the back of the leg that inserts into the heel.
The most common cause is over-pronation.
Treatment:
Athletes should use an orthotic device, heel cup, or heel cradle for extra support.
A heel cup or heel cradle elevates the heel to reduce stress and pressure on the achilles tendon. The device should be made with light-weight, shock absorbing materials. An orthotic device can be used to control over-pronation, support the longitudinal arch, and reduce stress on the achilles tendon.
Ingrown nails

Definition:
Known to physicians as onychocryptosis, ingrown toe nails are a common, painful condition that occur when skin on one or both sides of a nail grows over the edges of the nail, or when the nail itself grows into the skin. This condition is usually very painful and can be associated with infection of the toe. Some ingrown toenails are chronic, with repeated episodes of pain and infection. Irritation, redness, an uncomfortable sensation of warmth, as well as swelling can result from an ingrown toenail.
Treatment:
A podiatrist can trim or remove the infected nail with a minor in-office surgical procedure. He or she can remove the offending portion of the nail or overgrown skin with a scalpel and treat the infection. Unless, the problem is congenital, the best way to prevent ingrown toenails is to protect the feet from trauma and wear shoes with adequate room for the toes.